Discuss about the G7 nations agreed to adopt “risk-based” regulation on Artificial Intelligence (AI)
G7 nations agreed to adopt “risk-based” regulation on Artificial Intelligence (AI)
| “Risk” is understood as the combination of the likelihood of harm of any kind, and the potential magnitude and severity of this harm. Risk-based regulation is, crucially, about focusing on outcomes rather than specific rules and process as the goal of regulation. |
Why in News?
- At the end of a two-day meeting in Japan, the digital ministers of the G7 advanced nations recently agreed to adopt “risk-based” regulation on artificial intelligence (AI).
- Italy, a G7 member, had recently decided to ban ChatGPT due to privacy concerns but the ban was lifted.
What is the Group of Seven (G7)?
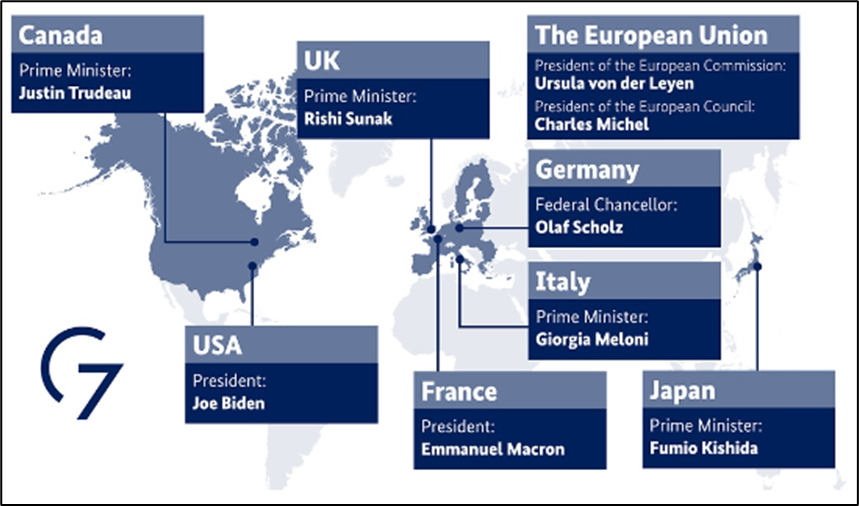
- It is an inter-governmental informal political forum of 7 wealthy democracies formed in 1975.
- It consists of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- It is officially organized around shared values of pluralism and representative government, with members making up the world’s largest International Monetary Fund (IMF) advanced economies in the world.
- The heads of government of the member states, as well as the representatives of the European Union (non-enumerated member), meet at the annual G7 Summit.
- As of 2020, G7 accounts for over half of global net wealth (at over $200 trillion), 30 to 43% of global GDP and 10% of the world’s population.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of a computer or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require human intelligence and discernment. Although there is no AI that can perform the wide variety of tasks an ordinary human can do, some AI can match humans in specific tasks.
- The ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self-algorithms etc.
Evolution
- In the year 1956, American computer scientist John McCarthy organized the Dartmouth Conference, at which the term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ was first adopted. From then on, the world discovered the ideas of the ability of machines to look at social problems using knowledge data and competition.
- Every aspect of science and especially when one starts looking at empowering machines to behave and act like human beings, the questions of ethics arise. About 70’s and late 80’s there was a time when the governments stopped funding research into AI.
- AI experienced a resurgence following concurrent advances in computer power and large amounts of data and theoretical understanding in the 21st century.
- AI techniques now have become an essential part of the technology industry helping to solve many challenging problems in computer-science. From Apple Siri to self-driving cars, AI is progressing rapidly.
Turing Test
The Turing Test was proposed in a paper published in 1950 by mathematician and computing pioneer Alan Turing. The Turing Test is a deceptively simple method of determining whether a machine can demonstrate human intelligence: If a machine can engage in a conversation with a human without being detected as a machine, it has demonstrated human intelligence.
What are the Different Categories of AI?
Artificial intelligence can be divided into two different categories:
- Weak AI/ Narrow AI: It is a type of AI that is limited to a specific or narrow area. Weak AI simulates human cognition. It has the potential to benefit society by automating time-consuming tasks and by analyzing data in ways that humans sometimes can’t. For example, video games such as chess and personal assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri.
- Strong AI: These are systems that carry on tasks considered to be human-like. These tend to be more complex and complicated systems. They are programmed to handle situations in which they may be required to problem-solving without having a person intervene. These kinds of systems can be found in applications like self-driving cars.
What are the Different Types of AI?
- Reactive AI:
- It uses algorithms to optimize outputs based on a set of inputs. Chess-playing AI, for example, are reactive systems that optimize the best strategy to win the game.
- Reactive AI tends to be fairly static, unable to learn or adapt to novel situations. Thus, it will produce the same output given identical inputs.
2. Limited Memory AI:
- It can adapt to past experiences or update itself based on new observations or data. Often, the amount of updating is limited, and the length of memory is relatively short.
- Autonomous vehicles, for example, can read the road and adapt to novel situations, even learning from past experience.
3. Theory-of-mind AI:
- They are fully adaptive and have an extensive ability to learn and retain past experiences. These types of AI include advanced chat-bots that could pass the Turing Test, fooling a person into believing the AI was a human being.
4. Self-aware AI:
- As the name suggests, become sentient and aware of their own existence. Still some experts believe that an AI will never become conscious or alive.
What is the Difference Between Augmented Intelligence and AI?
- The Difference in Focus: Artificial Intelligence is focused on creating machines that can perform tasks autonomously, without human intervention. On the other hand, Augmented Intelligence is the use of technology to enhance human intelligence, rather than replace it.
- Augmented Intelligence systems are designed to work alongside humans to improve their ability to perform tasks.
- The Difference in Goal: The goal of AI is to create machines that can perform tasks that require human intelligence, such as decision-making and problem-solving.
- The goal of Augmented Intelligence, on the other hand, is to enhance human capabilities, by providing them with tools and technologies that can help them make better decisions and solve problems more efficiently.
Applications of AI in Different Sectors?
- Healthcare: AI enhances diagnosis accuracy, enable personalized treatment, improve patient outcomes, streamline healthcare operations, and accelerate medical research and innovation.
- Business: AI in the business sector helps optimize operations, enhance decision-making, automate repetitive tasks, improve customer service, enable personalized marketing, analyze big data for insights, detect fraud and cybersecurity threats, streamline supply chain management, and drive innovation and competitiveness.
- Education: AI could open new possibilities for innovative and personalized approaches catering to different learning abilities. As demonstrated by ChatGPT, Bard and other large language models, generative AI can help educators and engage students in new ways.
- Judiciary: It is used to improve legal research and analysis, automate documentation and case management, enhance court processes and scheduling, facilitate online dispute resolution, assist in legal decision-making through predictive analytics, and increase access to justice by providing virtual legal assistance and resources.
- SUVAS (Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software): It is an AI system that can assist in the translation of judgments into regional languages.
- SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency): It was recently launched by the Supreme Court of India
- Cybersecurity/Security: It is used in security and cybersecurity to detect and prevent cyber threats, identify anomalous activities, analyze large volumes of data for patterns and vulnerabilities, enhance network and endpoint security, automate threat response and incident management, strengthen authentication and access control, and provide real-time threat intelligence and predictive analytics for proactive defense against cyber-attacks.
Benefits of AI:
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data with precision, reducing errors and improving accuracy in various applications, such as diagnostics, predictions, and decision-making.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI provides data-driven insights and analysis, assisting in informed decision-making by identifying patterns, trends, and potential risks that may not be easily identifiable to humans.
- Innovation and Discovery: AI fosters innovation by enabling new discoveries, uncovering hidden insights, and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in various fields, including healthcare, science, and technology.
- Increased Productivity: AI tools and systems can augment human capabilities, leading to increased productivity and output across various industries and sectors.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptability: AI systems can learn from new data and experiences, continually improving performance, adapting to changes, and staying up-to-date with evolving trends and patterns.
6. Exploration and Space Research: AI plays a crucial role in space exploration, enabling autonomous spacecraft, robotic exploration, and data analysis in remote and hazardous environments.
7. In Policing: AI based products open a new window of opportunity to do predictive policing. With the help of AI, one can predict the pattern of crime, analyze lot of CCTV footage to identify suspects.
What are the Differences Between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)?
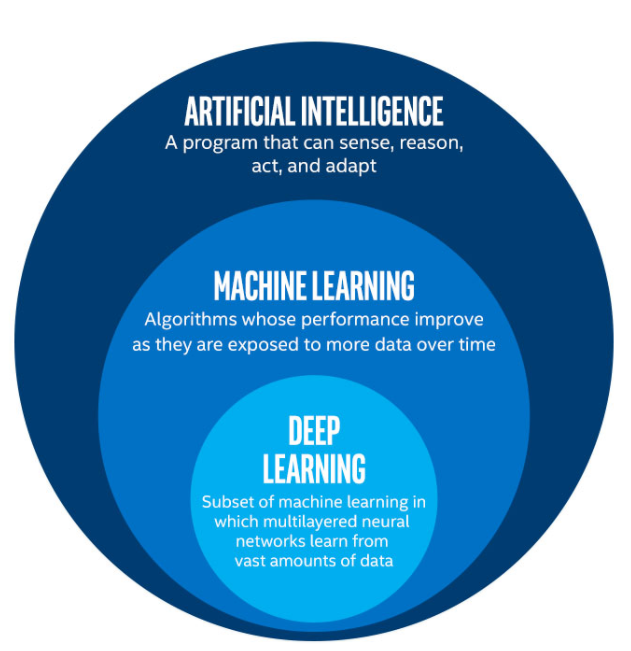
AI, ML and DL are common terms and are sometimes used interchangeably. But there are distinctions.
- ML is a subset of AI that involves the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms can analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions based on the patterns they find.
- DL is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data in a way that is similar to how the human brain learns.
What are the Ethical Considerations of AI?
Disadvantages of AI:
- Job Displacement: Because robots and algorithms can now execute tasks that previously required humans to perform them, AI automation may result in the displacement of some employment. This may lead to unemployment and call for the workforce to receive new training or skills.
- Ethical Concerns: AI raises ethical concerns such as the potential for bias in algorithms, invasion of privacy, and the ethical implications of autonomous decision-making systems.
- Reliance on Data Availability and Quality: AI systems heavily rely on data availability and quality. Biased or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate results or reinforce existing biases in decision-making.
- Security Risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks and exploitation. Malicious actors can manipulate AI algorithms or use AI-powered tools for nefarious purposes, posing security risks.
- Overreliance: Blindly relying on AI without proper human oversight or critical evaluation can lead to errors or incorrect decisions, particularly if the AI system encounters unfamiliar or unexpected situations.
- Lack of Transparency: Some AI models, such as deep learning neural networks, can be difficult to interpret, making it challenging to understand the reasoning behind their decisions or predictions (referred to as the “black box” problem).
- Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs: Implementing AI systems often requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure, data collection, and model development. Additionally, maintaining and updating AI systems can be costly.
Why there is need to regulate AI:
- Regulator vacuum:
- Currently, governments do not have any policy tools to halt work in AI development. If left unchecked, it can start infringing on – and ultimately take control of – people’s lives.
2. Increased use of AI & privacy:
- Businesses across industries are increasingly deploying AI to analyze preferences and personalize user experiences, boost productivity, and fight fraud. For example, ChatGPT Plus, has already been integrated by Snapchat, Unreal Engine and Shopify in their applications.
- This growing use of AI has already transformed the way the global economy works and how businesses interact with their consumers. However, in some cases it is also beginning to infringe on people’s privacy.
3. Fixing accountability:
- AI should be regulated so that the entities using the technology act responsible and are held accountable.
- Laws and policies should be developed that broadly govern the algorithms which will help promote responsible use of AI and make businesses accountable.
What can be the Way Forward?
- Ethical and Responsible AI: It is crucial to prioritize the development and deployment of AI systems that are ethical, transparent, and accountable. This includes addressing biases, ensuring privacy and data protection, and establishing clear regulations and guidelines.
- Continued Research and Innovation: AI is a rapidly evolving field, and ongoing research and innovation are necessary to advance its capabilities further. Investments in fundamental research, such as developing new algorithms and models, can lead to breakthroughs and improved performance.
- Data Quality and Accessibility: High-quality and diverse datasets are essential for training AI models effectively. Efforts should focus on improving data collection, cleaning, and labeling processes.
- Additionally, promoting data sharing and accessibility can foster collaboration and accelerate progress across different domains.
4. Human-AI Collaboration: AI should be designed to augment human capabilities rather than replace them entirely. Emphasizing human-AI collaboration can lead to more effective solutions and enhance productivity in various industries.
- User-centered design and interfaces that facilitate seamless interaction with AI systems are important considerations.
5. Domain-Specific Applications: Identifying and prioritizing specific domains where AI can have a significant impact is key. Tailoring AI solutions to address specific challenges in fields such as healthcare, transportation, finance, and education can yield tangible benefits and drive adoption.
6. Continued Education and Workforce Development: Preparing the workforce for an AI-driven future is crucial. Initiatives focused on AI education and upskilling programs can help individuals acquire the necessary skills to thrive in a changing job market.
- Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration and fostering partnerships between academia, industry, and government can further support these efforts.
7. International Collaboration and Standards: Collaboration across countries and organizations is essential for sharing knowledge, best practices, and addressing global challenges associated with AI. Establishing international standards and frameworks can ensure interoperability, fairness, and security in the development and deployment of AI systems.
Conclusion
AI has all the ability to surpass human intelligence and can perform any particular task much accurately and efficiently. There is also no doubt that AI possesses immense potential which further helps to create a better place to live in. However, anything in excess is not good and nothing can be matched at par with the human brain.
Therefore, AI should not be used excessively as too much automation and dependent on machines can create a very hazardous environment for the present human mankind and for the next generations to come.
Fibre Optic Technology
Why in news?
The growing need for high-speed internet connections has transformed Optical Fibres into the current reality of high-speed data transmission.
- During the pandemic, the crucial role of internet in maintaining global connectivity was highlighted which was facilitated largely by high-speed internet connections.
- Services such as online payments, virtual meetings, video calls etc highly depended upon the technology of optical fibres.
Understanding Fibre Optics:
-
- Optical Fibres are thin, cylindrical strands composed of glass, with a diameter typically comparable to that of a human hair.
- These fibres possess the remarkable ability to transmit various forms of information, including text, images, audio, video, phone calls, and any data that can be digitized, across vast distances at speeds approaching that of light.
- They are strong, lightweight, and remarkably flexible, making them suitable for burial underground, submersion underwater, or coiling around a spool.
- Almost 60 years ago, physicist Charles Kao proposed the concept of using glass Fibres as a superior medium for telecommunications, superseding the prevalent copper wires.
- His groundbreaking contributions to Fibre optic communication earned him a share of the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics.
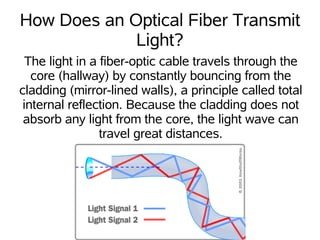
Working:
- Principle of Total Internal Reflection: The phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection (TIR) forms the basis for guiding light within optical Fibres.
If light travels from a higher refractive index medium (like glass) to a lower one (such as air) at a specific angle, it may not exit the medium but be entirely reflected back within it. This phenomenon is called TIR.
- Signal Encoding: Information is encoded into optical signals as rapidly blinking light pulses, typically representing binary digits (zeros and ones).
These optical signals are fed into one end of an optical Fibre, where they travel by reflecting and bouncing between the glass walls due to total internal reflection.
- Signal Transport: The optical Fibre carries the encoded signals across several kilometers without significant loss of signal integrity.
At the destination, a receiver reproduces the encoded information from the transmitted optical signal
Benefits:
-
- High Speed: Fibre provides more bandwidth and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps and beyond, something that it is impossible to achieve when using copper.
- More bandwidth means that Fibre can carry more information with far greater efficiency than copper wire.

- More bandwidth means that Fibre can carry more information with far greater efficiency than copper wire.
- Range of Transmission: Since data travels in the form of light in Fibre-optic cables, very little signal loss occurs during transmission and data can move at higher speeds and greater distances.
- Not susceptible to interference: Fibre-optic cable is also much less susceptible to noise and electromagnetic interference than copper wire.
- It is so efficient, in fact, that roughly 99.7% of the signal reaches the router in most cases.
- Durability: Fibre-optic cable is completely immune to many environmental factors that affect copper cable.
- The core is made of glass, which is an insulator, so no electric current can flow through.
- High Speed: Fibre provides more bandwidth and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps and beyond, something that it is impossible to achieve when using copper.
Applications of optical Fibres:
- Telecommunications: Optical fibers are the backbone of the modern telecommunications network, able to transmit data much faster and over longer distances than copper wires.
- Computer networking: Optical fibers are used to connect computers and servers within local area networks (LANs). They provide high-bandwidth connections essential for cloud computing, big data, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Cable television: Optical fibers are used to deliver cable television signals to homes and businesses.
- Medical imaging: Optical fibers are used in a variety of medical imaging devices, such as endoscopes, microscopes, and lasers.
- Sensor networks: Optical fibers are used to transmit data from sensors in a variety of applications, such as environmental monitoring, industrial automation, and in hazardous locations.
- Military and aerospace applications: Optical fibers are used for secure communications in hostile environments, missile guidance systems, and laser rangefinders.
- Scientific research: Optical fibers are used in spectroscopy, fiber optics sensing, and optical communication.
Future of Fibre Optics in India:
- Fibre optics technology has since been widely used in telecommunication, medical science, laser technology, and sensing.
- With a goal to securing communication and promoting quantum science, the Government of India announced a national mission in the Union Budget of 2020. The proposed budget for this ‘National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications’ is Rs 8,000 crore over a period of five years.
- The possibilities of fibre optic networks are growing at an accelerated rate, reaching all the way into our homes. Along with quantum optics, fibre optic communication stands on the cusp of a new era
