Discuss about the Global Carbon Budget
Global Carbon Budget
The sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change showed that the world can emit only about 500 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide (GtCO2) starting January 1, 2020 for a 50 percent chance of limiting warming to 1.5°C. For a 67 percent chance of avoiding 1.5°C, the budget will come down to 400 GtCO2.
|
Carbon Budget:
|
What is a global carbon budget?
- Global Carbon Budget refers to the permissible amount of CO2 emissions that humanity can release while still aiming to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, as stipulated by the Paris Agreement.
- It encompasses CO2 extracted from the atmosphere, regional carbon emissions, CO2 emissions from land use, and carbon emissions from various human-made projects.
- This budget is established within the framework of the Global Carbon Project (GCP).
- It is a component of the broader carbon cycle, illustrating how carbon is added to and subtracted from Earth’s carbon reservoirs.
- The estimated carbon budget is approximately 1 trillion tonnes
Importance of Global Carbon Budget:
- Clean energy- It encourages the development of alternative energy resources and more efficient ways to use energy, by making carbon-emitting fuels more expensive.
- Fund- It generates revenue that can be used to fund clean-energy technologies, compensate the affected people, or reduce other taxes.
- Limits global warming- It establishes how much CO2 can be emitted without exceeding the temperature goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Set targets- It helps to set emissions reduction targets in a fair and effective way, based on the scientific evidence and value judgments
- Climate science- It will help countries to stay within the remaining warming limit.
- Road to net zero- Governments can measure how well they are doing in reducing their climate impact.
- Impetus to CBDR- It boosts Common But Different Responsibilities (CBDR) that was formalized at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro
Initiatives by India:
- International Solar Alliance: It was a joint effort by India and France to mobilize efforts against climate change through deployment of solar energy solutions launched in 2015.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure: It is an international climate initiative by India in 2019 to promote resilient climate-proof critical infrastructure in member countries.
- Global Bio-fuel alliance: It is an alliance driven by India, the United States, and Brazil, to accelerated adoption of biofuels, creating new biofuels, setting globally recognized standards, identifying global best practices, and ensuring industry participation.
- LiFE Mission: Lifestyle for Environment is an international mass movement to protect and preserve the environment launched in COP 26 at Glasgow in 2021
CRISPR Technology
- Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) is a gene editing technology that mimics the natural defence mechanism in bacteria to combat virus attacks, utilizing a specialized protein known as Cas9.
- Typically, it entails the addition of a new gene or the inhibition of an existing gene through a procedure known as genetic engineering.
- CRISPR technology does not entail the incorporation of any external gene
More about the Technology:
- Described as ‘Genetic Scissors,’ CRISPR-Cas9 technology is frequently likened to the functionalities of ‘cut-copy-paste’ or ‘find-replace’ in common computer programs.
- In the process, a problematic segment in the DNA sequence, responsible for a disease or disorder, is identified, cut, removed, and then substituted with a ‘correct’ sequence.
- The tools employed for this procedure are biochemical, involving specific protein and RNA molecules.
- This technology emulates a natural defence mechanism found in certain bacteria, employing a similar approach to shield itself from virus attacks
Importance:
- Specific Treatment: CRISPR aids in the disease treatment by correcting the underlying genetic problem. CRISPR-based therapeutic solutions are not in the form of a pill or drug. Instead, some cells of every patient are extracted, the genes are edited in the laboratory, and the corrected genes are then re-injected into the patients.
- What is to be edited, and where, is different in different cases. Therefore, a specific solution needs to be devised for every disease or disorder that is to be corrected.
- The solutions could be specific to particular population or racial groups, since these are also dependent on genes.
- The changes in genetic sequences remain with the individual and are not passed on to the offspring.
- What is to be edited, and where, is different in different cases. Therefore, a specific solution needs to be devised for every disease or disorder that is to be corrected.
- Permanent Cure of Genetic Diseases/Anomalies: A vast number of diseases and disorders are genetic in nature i.e.; they are caused by unwanted changes or mutations in genes.
- These include common blood disorders like sickle cell anaemia, eye diseases including colour blindness, several types of cancer, diabetes, HIV, and liver and heart diseases. Many of these are hereditary as well.
- CRISPR opens up the possibility of finding a permanent cure for many of these diseases.
- Deformities like stunted or slow growth, speech disorders, or inability to stand or walk arise out of abnormalities in gene sequences.
- CRISPR presents a potential treatment for the cure of such abnormalities as well.
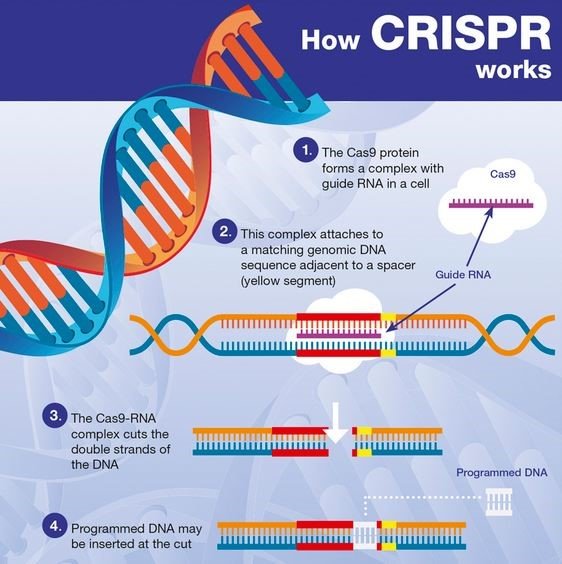
Functioning of CRISPR-Cas9 Technology:
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system consists of two key molecules that introduce a change into the DNA. These are:
- an enzyme called Cas9. This acts as a pair of ‘molecular scissors’ that can cut the two strands of DNA at a specific location in the genome so that bits of DNA can then be added or removed.
- a piece of RNA called guide RNA (gRNA). This consists of a small piece of pre-designed RNA sequence (about 20 bases long) located within a longer RNA scaffold. The scaffold part binds to DNA and the pre-designed sequence ‘guides’ Cas9 to the right part of the genome. This makes sure that the Cas9 enzyme cuts at the right point in the genome.
- The guide RNA is designed to find and bind to a specific sequence in the DNA. The guide RNA has RNA bases? that are complementary? to those of the target DNA sequence in the genome. This means that, at least in theory, the guide RNA will only bind to the target sequence and no other regions of the genome.
- The Cas9 follows the guide RNA to the same location in the DNA sequence and makes a cut across both strands of the DNA.
- At this stage the cell? recognises that the DNA is damaged and tries to repair it.
- Scientists can use the DNA repair machinery to introduce changes to one or more genes? in the genome of a cell of interest
Karmayogi Prarambh
About the Mission:
Launched on September 20, 2020, Mission Karmayogi – National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) is designed to bring about reforms in the Indian bureaucracy, addressing individual, institutional, and procedural aspects to enhance public service delivery. Its primary objective is to enhance the post-recruitment training system for government officers and employees at all levels.
The initiative is overseen by the Prime Minister’s Human Resource Council, which includes chief ministers, union cabinet ministers, and experts. The council reviews and approves civil service capacity-building programs. A Capacity Building Commission is responsible for formulating and overseeing annual capacity-building plans and conducting audits of human resources within the government.
Significance of Rozgar Mela:
- The Rozgar Mela is an initiative of the central government to provide employment opportunities to the youth of the country.
- Under the Rozgar Mela Scheme, 10 lakh jobs will be available for candidates to apply in Group A and B Gazetted Posts, Group B Non-Gazetted and Group C Non-Gazetted posts.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) would also fill a significant number of posts in various Central Armed Police Forces.
- These recruitments are being done in mission mode by ministries and departments either by themselves or through recruiting agencies such as UPSC, SSC and Railway Recruitment Board.
|
Karmayogi Prarambh Module:
|
