Prelims – 14th Nov 23
Biofuel:
- Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil.
- Since biomass can be used as a fuel directly (e.g., wood logs), some people use the words biomass and biofuel interchangeably.
- However, the word biofuel is usually reserved for liquid or gaseous fuels, used for transportation.
- Most of biofuel consumption occurs as a blend with refined petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel fuel, heating oil, and kerosene-type jet fuel.
- However, some biofuels do not require blending with their petroleum counterparts and are referred to as drop-in biofuels.
- The most common biofuels now are –
- Bioalcohols such as ethanol, propanol, and butanol (a substitute for petrol/gasoline);
- Biodiesel (a substitute for diesel);
- Bio-oils (substitutes for kerosene).
Generations of Biofuel:
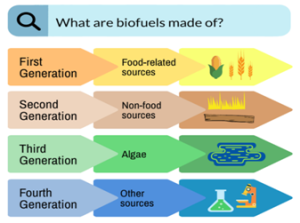
- Biofuels are also divided into four categories depending on their origin and production technologies.
- First Generation–
- 1G biofuels are produced from consumable food items containing starch (rice and wheat) and sugar (beets and sugarcane) for bioalcohols, or vegetable oils for biodiesel.
- However, the yields of 1G biofuels are low and can have negative impacts on food security.
- Second Generation–
- 2G biofuels are mainly obtained from non-food feedstocks such as forest/industry/agricultural wastes and waste or used vegetable oils.
- Third Generation –
- 3G biofuels, known as ‘algae fuel’, are derived from algae in the form of both, biodiesel and bioalcohols.
- Although the yield of 3G biofuels is approximately 10 times higher than 2G biofuels, producing adequate algal biomass and scaling up extraction techniques are as yet unresolved challenges.
- Fourth Generation –
- Like the third generation, 4G biofuels are made using non-arable land.
- However, unlike the third, they do not need the destruction of biomass.
- This class of biofuels includes electro fuels and photo-biological solar fuels.
- Like the third generation, 4G biofuels are made using non-arable land.
Citizen Charter
The Citizen’s Charter is a voluntary and written document that spells out the service provider’s efforts taken to focus on their commitment towards fulfilling the needs of the citizens/customers.
Components of Citizen charter:
A Citizen charter have following details –
- Organization’s vision and mission statements.
- Explain who are citizens and clients.
- Statement of services including quality, time-frame, etc. offered to citizens and how to get those services.
- Grievance redressal mechanisms.
- Additional commitments like the amount of compensation in case of service delivery failure., etc.
Free trade agreement
A Free trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more countries where the countries agree on certain obligations that affect trade in goods and services, and protections for investors and intellectual property rights, among other topics.
Significance of FTAs:
- FTAs encourage businesses in member nations to concentrate on manufacturing and selling the goods that best employ their resources.
- FTAs encourage the production and consumption of goods that are traded internationally by lowering the cost at which some items are produced in each nation.
- FTAs make it easier to blend domestic and international trade, which promotes economic growth.
- By making it simpler and less expensive for more enterprises to conduct international business, FTAs aid in the diversification of supply chains.
- Reducing the trade barriers will help small and medium-sized enterprises in the export of their goods and services and also gives them access to new and emerging technologies.
- Consumers in both nations would benefit from improved product variety and affordability thanks to FTAs.
- FTAs encourage Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) which helps in capital flow and employment creation.
- FTAs play an important role in strengthening the bond between the countries.
