Prelims – 19th Nov 23
Sanchi Stupa
- It was built by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in the third century BC.
- It enshrines religious relics or remains of the Buddha and his most revered disciples.
- Structure:
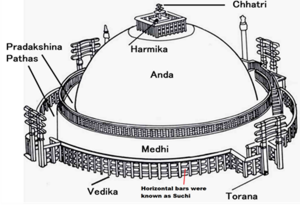
- It is enclosed by a massive stone railing pierced by four gateways, which are adorned with elaborate carvings (known as Sanchi sculpture).
- The stupa itself consists of a base bearing a hemispherical dome (anda), symbolizing the dome of heaven enclosing the earth.
- It is surmounted by a squared rail unit (harmika) representing the world mountain, from which rises a mast (yashti), symbolizing the cosmic axis.
- The mast bears umbrellas (chatras) that represent the various heavens (devaloka).

Corporate Social Responsibility
- It is a business model by which companies make a concerted effort to operate in ways that enhance rather than degrade society and the environment.
- It helps both improve various aspects of society as well as promote a positive brand image of companies.
- Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 makes it mandatory for the following companies having in the immediately preceding financial year:
- Every company having a net worth of rupees five hundred crores or more, or
- Every company having a turnover of rupees one thousand crores or more, or
- Every company has a net profit of rupees five crores or more to comply with CSR provisions.
Just Energy Transition Partnership (JET-P)
- It is a mechanism for multilateral financing by developed countries to support an energy transition in developing countries.
- It aims to reduce emissions in the energy sector and accelerate the coal phase-out.
- Transition describes the gradual movement towards lower carbon technologies, while ‘Just’ qualifies that this transition will not negatively impact society, jobs and livelihoods.
- It was launched at the COP26 in Glasgow with the support of the United Kingdom (UK), the United States (US), France, Germany, and the European Union (EU).
- Senegal has become the fourth country after South Africa, Indonesia and Vietnam to sign the JET-P deal, with the International Partners Group comprising France, Germany, the European Union, the United Kingdom and Canada.
- India refused to give its consent, saying that coal cannot be singled out as a polluting fuel and that energy transition talks need to take place on equal terms.
