Prelims 25-01-2024
Topic 1: The project ‘AMBER’
What is project ‘AMBER’?
- It stands for Accelerated Mission for Better Employment and Retention (AMBER) project.
- It is a joint initiative of the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) in collaboration with Generation India Foundation (GIF) and Amazon Web Services India Private Limited (AWS India).
- The initiative has been undertaken under the SANKALP programme of MSDE with a focus on women to improve gender diversification in the tech industry and underprivileged groups.
What does the project aim to achieve?
It aims to train 30,000 youth, 50% of whom will be women trainees.
- The training will be conducted in post-COVID resilient job roles, over a period of two years. Generation’s holistic 7-step skilling methodology will be utilised to drive higher quality skilling, improved employment, and retention outcomes.
- It will help building capabilities in areas that are evolving due to demographic transitions and technological changes such as Industry 4.0 and Web 3.0.
How does collaboration with industries going to help skill women and youth?
Collaborating with AWS re/Start is crucial for those individuals who need cloud computing skills and to open up more opportunities for women to pursue tech careers.
- As part of this collaboration, the learners take part in AWS (re/Start), a workforce development program that covers fundamental cloud computing skills as well as practical career tips.
- The skilling will be through real-world scenario-based exercises, labs, and coursework, learners are trained in multiple technologies, including Linux, Python, networking, security, and relational databases. Thus making them industry ready.
- The program also covers the cost for learners to take the AWS Cloud Practitioner Certification exam, an industry-recognized credential that validates their cloud skills and knowledge and connects the participants with job interview opportunities in cloud or IT with local employers.
Topic 2: Ozone Layers in Troposphere
How is ozone formed in the atmosphere?
Ozone (composed of three atoms of oxygen) is a gas that occurs both in the Earth’s upper atmosphere and at ground level.
- Ozone is formed throughout the atmosphere in multistep chemical processes that require sunlight. In the stratosphere, the process begins with an oxygen molecule (O2) being broken apart by ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
- In the lower atmosphere that is troposphere, ozone is formed by different set of chemical reactions involving hydrocarbons and nitrogen-containing gases.
Thus, ozone layer can be classified in two types:
- Stratospheric ozone
- Tropospheric ozone
Ozone can be “good” or “bad” for health and the environment, depending on its location in the atmosphere. Stratospheric Ozone protects us from UV radiation where as Tropospheric ozone is a pollutant and hazardous to human health.
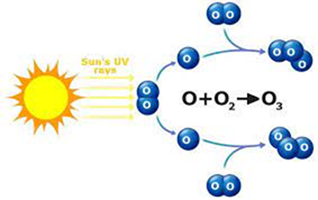
What is Stratospheric ozone and how its formed?
- Stratospheric ozone is naturally formed in chemical reactions involving ultraviolet sunlight and oxygen molecules, which make up 21% of the atmosphere.
- In the first step, sunlight breaks apart one oxygen molecule (O2) to produce two oxygen atoms (2O).
- In the second step, each atom combines with an oxygen molecule to produce an ozone molecule (O3). These reactions occur continually wherever ultraviolet sunlight is present in the stratosphere. As a result, the greatest ozone production occurs in the tropical stratosphere.
How is tropospheric ozone formed?
- Tropospheric, or ground level ozone, is not emitted directly into the air, but is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC). Fossil fuel combustion is a primary pollution source for tropospheric ozone production.
NOx + VOC + sunlight yields -> O3
- Typically, ozone levels reach their peak in mid to late afternoon, after exhaust fumes from morning rush hour have had time to react in sunlight. A hot, sunny, still day is the perfect environment for the production of ozone pollution. At the end of the day, as the Sun starts to set, the production of ozone begins to subside. To form, ozone needs sunshine to fuel the chemical reaction.
What are the Problems associated with tropospheric ozone?
Ozone is harmful to all types of cells. It can impair an athlete’s performance, create more frequent attacks for individuals with asthma, cause eye irritation, chest pain, coughing, nausea, headaches and chest congestion. It can worsen heart disease, bronchitis, and emphysema. When it’s inhaled, ozone can damage lung tissues.
Ozone also damages materials like rubber, textile dyes, fibers, and certain paints. These materials can be weakened or degraded by exposure to ozone. Some elastic materials can become brittle and crack, while paints and fabric dyes may fade more quickly.
What steps are needed to decrease formation of ozone in troposphere?
Various steps have been taken by the government to mitigate pollutant responsible for formation of tropospheric ozone. These are:
- Banning of garbage burning, rather waste management needs to be done in an ecological manner.
- Reduction is vehicular pollutant, through shifting to BS-VI compliant vehicles from BS-IV.
- Encouraging and facilitating production of greener fuel and technology through right policies and practices. Example ethanol blending program and green hydrogen.
