Prelims – 25th Oct 23
Genomics
Genomics is the study of all of a person’s genes (the genome), including interactions of those genes with each other and with the person’s environment.
The field of genomics uses biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology methods to understand and use biological information in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
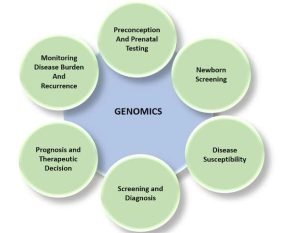
Genomics: a new era of evidence-based healthcare management system:
- In low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) with a high population density, such as India, the burden of infectious diseases continues to remain considerably high. The COVID-19 pandemic has been a wake-up call for individuals and healthcare systems, towards the urgent need for preventive healthcare.
- Tremendous advancements in science and technology such as genetic medicine, targeted therapy and mRNA/protein vaccines, imply that the world is moving towards “New Biological Entities (NBEs)”, which is a significant departure from the traditional “New Chemical Entities (NCEs)”.
- However, our ability to deliver new age, precision therapies, will depend on our ability to employ new age precision diagnostics, enabled by new age platform technologies such as genomics, wearables and point-of-care tests.
- Genomics and its adoption in clinical practice has seen a resurgence over the past few years, enabled largely by the completion of the Human Genome Project and other global studies which has increased its application to a wide array of conditions.
- Genomic information can not only allow us to study the individual genetic makeup, but also be used as a screening mechanism to determine health conditions and improve outcomes by identifying the correct treatment options for patients.
India Infrastructure Development Fund
- The scheme was notified by Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme which will aid the development of quality PPP projects by providing necessary funding support to the project sponsoring authorities, both in the Central and State Governments.
- The corpus of the IIPDF shall comprise of initial budgetary outlay of Rs. 100 Crore by the Ministry of Finance. This would be supplemented, should it become necessary, through budgetary support by the Ministry of Finance from time to time.
- The IIPDF will contributes upto 75% of the project development expenses to the Sponsoring Authority as an interest free loan. The balance 25% will be co-funded by the Sponsoring Authority.
- Funding under IIPDF Scheme is in addition to the already operational Scheme for Financial Support to PPPs in Infrastructure (VGF Scheme).
- The Public Private Partnership Cell of the DEA will provide support functions examine the applications received for assistance under IIPDF.
Measures of Money Supply
- M1 = Currency with Public + Demand Deposits with the banking sector + other deposits with RBI
- M2 = M1 + savings deposits with post office saving banks
- M3 = M1 + net time deposits with the banking system
- M3 is also known as aggregate monetary resources and broad money.
- M4 = M3 + total deposits with the post office savings organization (excluding National Savings Certificates).
- M0 (Reserve Money) = Currency in circulation + Bankers’ deposits with the RBI + Other deposits with the RBI
Reserve Money
Total liability of the monetary authority of the country, RBI, is called monetary base or high powered Money. This is basically claims which the general public, government or banks have on RBI and hence are considered to be the liability of RBI.
