Prelims – 27th Nov 23
Operation Samudragupt
- Operation Samudragupt was launched by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) in January 2022, to intercept contraband that is brought into India through the marine channel
- It is part of the Union government’s plan to make India drug-free by 2047
- The operation has been initiated by inputs from sources developed by the Naval Intelligence and the NCB.
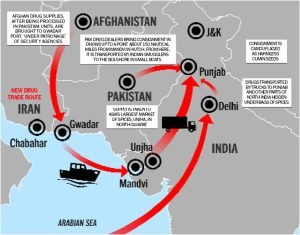
Methamphetamine
- Methamphetamine (meth) is an addictive drug and can cause considerable health adversities that can sometimes result in death
- It is used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, a sleep disorder
- Methamphetamine on its own might not cause the heart attack but it can result in a cardiac arrest if consumed in an excess quantity.
Narcotic Control Bureau (NCB)
- It was constituted by the Government of India in 1986 under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985
- It is the apex coordinating agency under the Ministry of Home Affairs
- Drug abuse control is the responsibility of the central government
- It has all the powers of a civil court trying a suit under the code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Campaign
- Launched in 2020, in 272 identified districts
- It is a three-pronged attack combining the supply curb by NCB, Outreach and Awareness and Demand Reduction effort by Department of Social Justice and Empowerment and treatment through Health Department.
e-VIGIL App
- Facilitates citizens to report MCC violations such as bribery, gifts, liquor distribution etc.
- Developed by ECI.
- MCC is set of guidelines issued by the ECI to regulate political parties and candidates prior to elections.
- The MCC is operational from the date on which the election schedule is announced until the date of the result announcement.
- It originated from Assembly elections of Kerala in 1960.
- From 1991 ECI decided to enforce MCC more strictly.
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea (BVD)
- BVD is an infectious disease, globally distributed endemic to cattle and other ruminant populations.
- It is caused by the Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus (BVDV).
- Most animals become exposed through contact with other recently infected or persistently infected (carrier) animals that are shedding the virus.
- While this virus has no cure, practising supportive therapies will temporarily help to improve the well-being of the cattle. Infected calves should be culled to prevent the spread of BVD.
- Scientists have recently created the first gene-edited calf with resistance to the bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV).
