Prelims – 29th Oct 23
James Webb Telescope
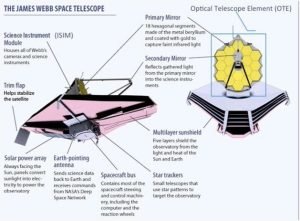
The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is an orbiting infrared observatory. It is the world’s most powerful ‘telescope’.
The telescope is the result of an international collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency. It is named after James E. Webb, who was the administrator of NASA from 1961 to 1968 during the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs.
Objective of the Webb:
- Search for the galaxies that formed the very beginning after the Big Bang.
- Determine the evolution of galaxies from their earlier formation until now.
- Observe the stages of the formation of stars until the formation of planetary systems.
- Measure the physical and chemical properties of planetary systems and investigate the potential for life in such systems.
Unique features of James Webb telescope:
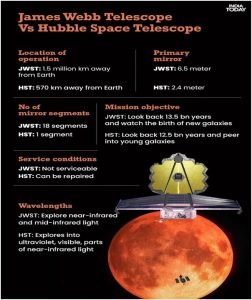
- The James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope, with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity.
- The longer wavelengths enable Webb to look much closer to the beginning of time and to hunt for the unobserved formation of the first galaxies, as well as to look inside dust clouds where stars and planetary systems are forming today.
- JWST is designed primarily to conduct infrared astronomy. Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation.
- As the largest optical telescope in space, its greatly improved infrared resolution and sensitivity allows it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope.
Minimum Support Price
The MSP is the rate at which the government purchases crops from farmers, and is based on a calculation of at least one-and-a-half times the cost of production incurred by the farmers.
MSP for a crop is the price at which the government is supposed to procure/buy that crop from farmers if the market price falls below it.
Crops Included
The Commission for Agricultural Costs & Prices (CACP) recommends MSPs for 22 mandated crops and fair and remunerative price (FRP) for sugarcane. The mandated crops include 14 crops of the kharif season, 6 rabi crops and 2 other commercial crops.
Crops covered by MSPs include:
- 7 types of cereals (paddy, wheat, maize, bajra, jowar, ragi and barley),
- 5 types of pulses (chana, arhar/tur, urad, moong and masur),
- 7 oilseeds (rapeseed-mustard, groundnut, soyabean, sunflower, sesamum, safflower, nigerseed),
- 4 commercial crops (cotton, sugarcane, copra, raw jute)
Biological Diversity Act 2002
- Following person shall require previous approval of National Biodiversity Authority before obtaining any biological resource in India:
- Any foreign citizen
- Indian citizen but not resident as per Income Tax Act 1961
- Body corporate or organisation not registered in India
- Body corporate or organisation registered in India, but has non-Indian participation in its share capital
- Everyone has to obtain prior approval of NBA if they want to apply for IPR based on research or info on a biological resource obtained from India.
- Apart from Chairman, there are 3 ex-officio members:
- One representing Min of Tribal Affairs
- Two representing Min of EFCC.
- NBAàSBAàBMC
- BMC is mandated to prepare People’s Biodiversity Register.
- Biodiversity Heritage sites can be notified by SG in consultation with BMC.
- If biological resource is obtained from India and invention has been based on it, then applying for IPR requires prior approval of NBA.
Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET)
- India and the United States have taken a significant step towards strengthening their strategic partnership and driving technology and defense cooperation.
- The iCET was announced by India and the US in May 2022 and was officially launched in January 2023 and is being run by the National Security Council of both countries.
- Both countries have identified six areas of cooperation which would include co-development and co-production, that would gradually be expanded to QUAD, then to NATO, followed by Europe and the rest of the world.
- It aims to promote collaboration in critical and emerging technology areas, including AI, quantum computing, semiconductors, and wireless telecommunication.
