Prelims – 30th Oct 23
Belt and Road Initiative
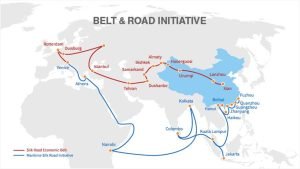
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a series of economic programmes designed by the Chinese government to foster economic cooperation along the ‘new Silk Road’, which stretches from the Chinese coast through to Europe. Announced at the end of 2013 by Chinese President Xi Jinping, it marks the most ambitious domestic and foreign policy programme ever initiated by the Chinese Communist Party.
Since the mid-2000s the Indian government has shunned its traditional non-alignment in favour of multialignment as a means of promoting their own national interests. Under those principles a strong relationship with China and investment into the BRI should be obvious, however Indian national security concerns have prevented any serious investment into the infrastructure programmes. The reason for such stand of India are as following:
- India views BRI initiatives as counter to its security interests. China-Pakistan relations and China Pakistan Economic Corridor running in PoK is case in point.
- India has repeatedly stated that it will not join BRI because it doesnot offer a level playing ground to the country’s businesses.
- Some of India’s neighbours – such as Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh – have received funding from China. India has resisted joining the initiative over fears that it will boost China’s strategic presence in the region.
- India is apprehensive of String Pearls policy of China whereby India is getting encircled by Chinese presence at strategic ports in Indian Ocean.
- The debt diplomacy that China is pursuing through its BRI has been criticized by India. India stated that connectivity initiative must follow principles of financial responsibility.
- The other issue that India has with countries in the region joining the BRI is the lack of transparency in the projects that China is investing in and the terms and conditions of loans being given by Beijing.
Semiconductor
Semiconductors, sometimes referred to as integrated circuits (ICs) or microchips, are made of compounds like gallium arsenide or pure elements like silicon or germanium. Doping is the addition of minute quantities of impurities to these pure elements, which significantly alters the material’s conductivity.
Importance of semiconductor in modern electronics
- Diode and Transistor: The most common semiconductor component is the diode, which allows current to flow in only one direction and thus functions as a one-way electronic valve. Following the diode, the transistor, which is used for fast switching or current amplification, was invented.
- Healthcare: The medical field uses advanced technology. Complex and risky surgeries are safer with the help of machines, operating with precision. Monitors and pacemakers are popular too. Even talking to patients and diagnosing symptoms is possible through video conferencing alone.
- Computing: Before the widespread use of silicon-based chips, computers were large machines with tubes and dials. Semiconductor chips replaced tubes, making machine management faster, cheaper, and more efficient. Microprocessors, memory, and graphic processing units (GPUs) are all common computer semiconductors.
- Telecommunication: A smartphone’s semiconductor chips affect its display, navigation, battery use, 4G reception, and more.
- Banking: Banks need semiconductors for accounting, ATMs, security cameras, and even automated locking mechanisms.
- Nanotechnology: The invention of the diode and transistor paved the way for nanotechnology, and new integrated chips such as microcontrollers, ULN2003, CD4050, and so on were developed.
- Household Appliances: Fridges, microwaves, washing machines, air conditioners, and other machines around the home and office operate on semiconductors.
Maritime Security
India’s 7,516-kilometre-long coastline includes 5,422 kilometres of coastline on the mainland and 2,094 kilometres on the islands belonging to nine states and four Union Territories.
The coastline accounts for 90% of the country’s trade and houses 12 major and 200 minor ports. This has necessitated the adoption of a more structured and holistic approach to modernise, update and strengthen coastal security architecture.
Security challenges emerging from India’s coastline:
- Maritime terrorism – hijacking, attacking, and sinking ships, taking hostages, sabotaging pipelines, and attacking cities and strategic installations like naval bases and petrochemical storages. For example – the 26/11 terror strike in Mumbai in 2008.
- Piracy and armed robbery pose a major threat to sea navigation. Shallow waters of the Sunderbans have been witnessing acts of violence and armed robbery.
- Indian coasts have been susceptible to smuggling of items such as gold, electronic goods, narcotics, and arms.
- Large scale of infiltration, illegal migration and refugee influx have resulted in widespread political turmoil in the border states. For example – the creek areas of Gujarat has complex terrain conducive for infiltration.
- The frequent straying of fishermen into neighbouring country waters has not only jeopardised the safety of the fishermen but has also raised national security concerns.
Zero Budget Natural Farming
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZNBF), popularized by Maharashtrian agriculturist and Padma Shri recipient Subhash Palekar, refers to the process of raising crops without using any fertilizers and pesticides or any other external materials.
The term ‘Zero Budget’ means the zero cost of production of all crops. ZBNF guides the farmers in practicing sustainable farming that helps in retaining soil fertility to ensure chemical-free agriculture and ensure low cost of production (zero-cost).

Benefits of ZBNF:
- ZBNF processes require 50–60 per cent less water and less electricity (than non-ZBNF) for all the selected crops.
- ZBNF reduces methane emissions significantly through multiple aeration.
- It also has the potential to avoid residue burning by practicing mulching.
- The cost of cultivation is lower in ZBNF. Thus increasing farmers income.
