Status of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
Status of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
Why in News?
A recent study conducted by the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has shed light on the growing burden of NCDs in India.
- The study marks the first comprehensive epidemiological research paper to include participants from 31 states and Union Territories. By including data from a wide range of regions, the study provides valuable insights into the prevalence and impact of NCDs, such as diabetes in the country
- The new national estimates for diabetes and other non-communicable diseases (NCD) shows that 31 million more Indians became diabetic in four years (2019-2021)
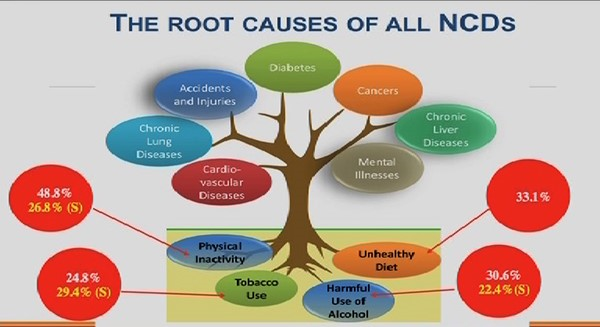
NCDs
|
Key Findings:
- Goa, Puducherry, and Kerala have the highest prevalence of diabetes, with rates approaching 25-26.4%.
- Diabetes: India now has 101 million individuals with diabetes.
- Prediabetes: The study identified 136 million people with pre-diabetes.
- High blood pressure: 315 million individuals were found to have hypertension.
- Obesity: 254 million people were classified as generally obese, while 351 million had abdominal obesity.
- The prevalence of generalised obesity stands at 28.6% across the population, while abdominal obesity affects 39.5% of Indians. Female abdominal obesity is particularly high, at 50%.
- Hypercholesterolemia: 213 million individuals had fat accumulation in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes
- The study reveals that 24% of Indians suffer from hypercholesterolemia.
- High LDL Cholesterol: 185 million individuals had elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
- LDL is the “bad cholesterol” because too much of it in blood can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Cholesterol travels through the blood on proteins called “lipoproteins
Significance of the Study:
- The study encompasses a large sample size of 1,13,043 individuals from diverse regions.
- It reveals that diabetes and other metabolic NCDs are more prevalent in India than previously estimated.
- While urban areas currently have higher rates of metabolic NCDs, except for prediabetes, rural regions are expected to experience a surge in diabetes cases in the next five years if left unregulated
Impact on Quality of Life and Life Expectancy:
- NCDs, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and chronic respiratory diseases, contribute to the overall disease burden in the country.
- NCDs often result in disabilities, reducing individuals’ functional abilities and impairing their daily activities.
- The management of NCDs requires long-term medical care, medications, and lifestyle modifications, which can be challenging for individuals and their families.
- NCDs can lead to increased healthcare expenses, impacting the financial well-being of individuals and households.
- The burden of NCDs can hinder individuals’ productivity and socioeconomic development, affecting their employment opportunities and economic growth.
- NCDs can significantly reduce life expectancy if not properly managed and controlled
What is the way forward?
- The answer to this developing pandemic, is in wellness and in having a lifestyle that encompasses healthy diet and exercise. NCDs have also been one of the major concerns of the Health Ministry.
- It has identified the four major NCDs — cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes. They all share four behavioural risk factors — unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and use of tobacco and alcohol.
- Programmes have been brought in to strengthen health infrastructure, human resource development, health-promotion and awareness-generation for prevention, early diagnosis and ensuring referrals to appropriate healthcare facilities for treatment of NCDs
State-Sponsored Cyber Attacks
Why in news?
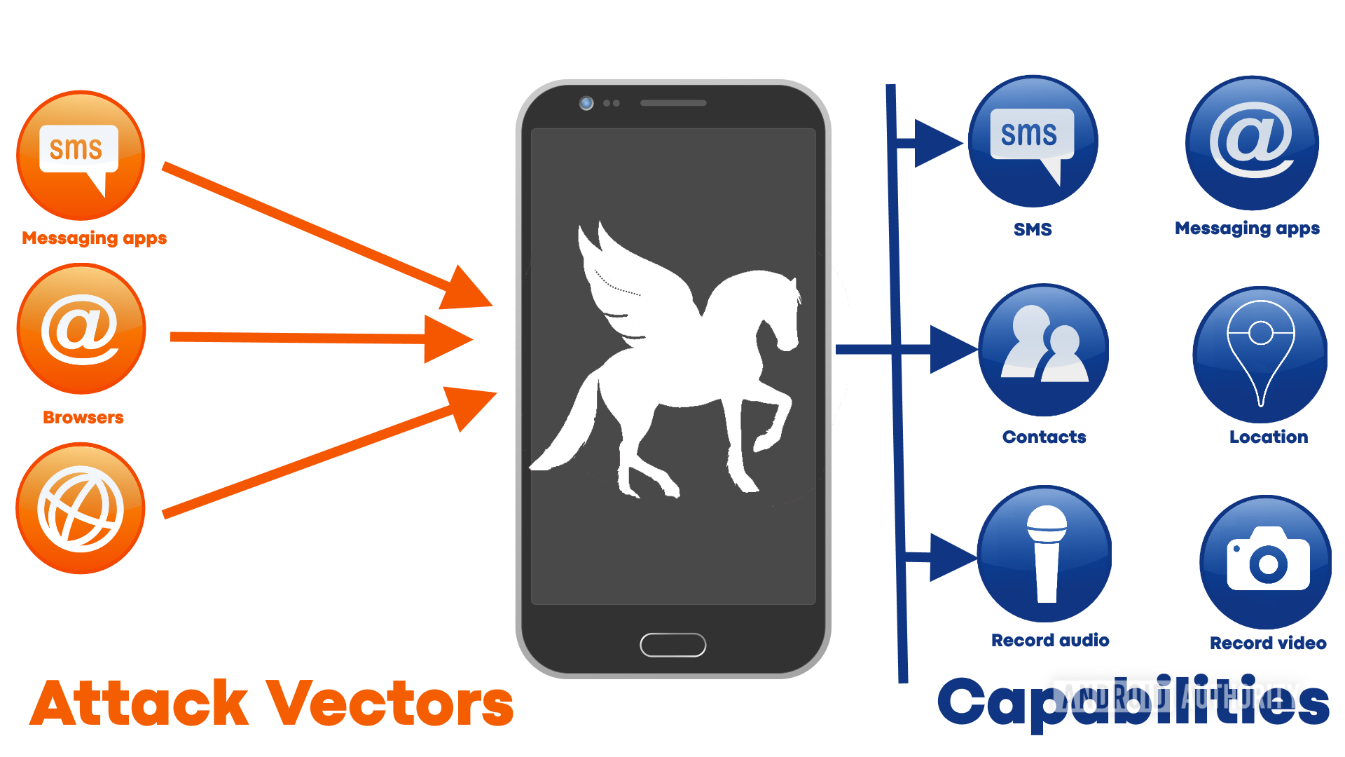
Automated notifications from Apple have been dispatched to individuals globally, encompassing numerous politicians and opposition leaders, cautioning them about possible state-sponsored attacks.
What are State-Sponsored Cyber Attacks?
-
About:
- State-sponsored cyber attacks, are cyberattacks conducted or supported by governments or government agencies against other nations, organizations, or individuals.
- These attacks are characterized by their high level of sophistication, organization, and resources, as they are backed by the extensive capabilities and funding of a nation-state.
- Examples of state-sponsored cyberattacks include the Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iran’s nuclear program, the alleged Russian interference in the 2016 U.S. presidential election, and the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, which was linked to North Korea.
-
Implications on National Security:
- Data Theft: State-sponsored attacks can lead to the theft of sensitive national security information, military secrets, and critical infrastructure data. Such breaches can compromise a nation’s defense capabilities.
- Economic Impact: Attacks on key industries and critical infrastructure can result in economic losses. For instance, the disruption of energy or financial systems can have severe economic consequences.
- Political Influence: Cyberattacks can be used to manipulate public opinion, influence elections, and undermine political stability. Disinformation campaigns and hacking can have far-reaching political implications.
- National Sovereignty: Cyberattacks can infringe upon a nation’s sovereignty and compromise its ability to govern and protect its citizens
Initiatives to contain such Cyber-Attacks
International Efforts:
- Budapest Convention on cybercrime:1st international treaty to address cybercrime; India is not a signatory.
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN):US-based not-for-profit organisation for coordinating & maintenance of several databases.
- Internet Governance Forum: UN forum for multi-stakeholder policy dialogue on Internet governance issues.
Apple recommendation (in the present case): They recommend activating Lockdown Mode, a feature introduced in recent software updates (iOS) to protect against rare and sophisticated cyber-attacks. Lockdown Mode restricts certain functions to enhance security
Indian Efforts:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC).
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
- Computer emergency Response Team – India (CERT-In)
Way Forward
There is a need to develop and implement comprehensive national cybersecurity policies and strategies that address both defense and offense in the cyber domain.
Allocate resources to bolster cybersecurity infrastructure, including advanced intrusion detection systems, secure networks, and cybersecurity training for government agencies.
Collaborate with other nations and international organizations to share threat intelligence and coordinate responses to state-sponsored threats