Initial Public Offering (IPO)
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has halved the listing time for Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) to three days from six days.
- It will come into effect from December 1, 2023.
- Objectives: This is likely to benefit issuers by allowing them to receive their funds faster and allottees to receive their securities in a shorter time period.
- SEBI has also tightened the disclosure norms for foreign portfolio investors (FPIs), requiring them to disclose their holdings of Indian securities on a real-time basis.
- This is aimed at improving transparency and preventing market manipulation.
- IPO: It is a process through which a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time, thereby transitioning from being privately held to becoming a publicly traded company.
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation Act, 2023
- The Rajya Sabha on Wednesday passed the Anusandhan National Research Foundation Bill.
- The Act repeals the Science and Engineering Research Board Act, 2008 and dissolves the Science and Engineering Research Board set up under it.
- Functions of NRF: NRF will be the apex body in the country to provide strategic direction for research, innovation, and entrepreneurship
- Fields: Natural sciences, engineering and technology, environmental and earth sciences, health and agriculture, scientific and technology interfaces of humanities and social sciences.
- Governing Council: NRF’s functioning will be governed by an Executive Council chairedby the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India.
Amendment to Wildlife Protection Act
Changes
- Currently, the Act has six schedules for specially protected plants (one), specially protected animals (four), and vermin species (one). Act reduces it to four by:
- Reducing the number of schedules for specially protected animals to two (one for greater protection level)
- Removes the schedule for vermin species
- Inserts a new schedule for specimens listed in the Appendices under CITES (scheduled specimens).
- Section 43 of the act amended which permitted the use of elephants for ‘religious or any other purposes’.
- Central government is empowered to regulate and stop the import, trade or possession of invasive plant or animal alien species.
- Central Government is authorised to designate a Management Authority which will grant export or import permits for the trade of specimens.
- One Scientific Authority will also be appointed to advice on aspects related to the impact on the survival of the specimens being traded.
- It empowers the central government to regulate or prohibit the import, trade, possession or proliferation of invasive alien species.
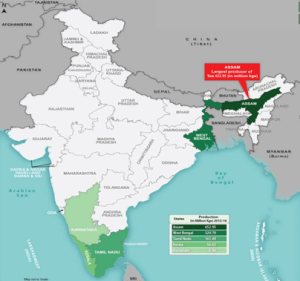
Indian Tea Industry
- India is the 2nd largest tea producer and largest black tea producer after China and 4th largest exporter of Tea in the world.
- India is also the largest consumer of black tea and accounts for 18% of the total World tea consumption.
- The main tea-growing regions are in the Northeast (including Assam) and in north Bengal (Darjeeling district and the Dooars region).
- Tea is also grown on a large scale in the Nilgiris in south India.
Ideal climate condition for tea cultivation:
- Originate in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Major tea growing regions are mainly concentrated in Asia, Africa, South America.
- Tea requires cool to warm temperatures with at least 5 hours of sunlight per day.
- The average annual temperature for tea plants to grow well is in the range of 15 – 23°C.
- The rainfall needed is between 150-200 cm.
Market Size of Tea Industry in India:
- In 2020, nearly 10 million tons of tea was consumed in the country.
- The market in the country is projected to witness a further growth in the forecast period of 2022-2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.2%.
- In 2026, the tea industry in India is expected to attain 1.40 million tons.
Tag for Geographical Indication (GI)
- The first GI tag product was Darjeeling Tea, also known as the “Champagne of teas” due to its floral aroma.
- Green and white tea, the other two Darjeeling tea varieties, also have GI tags.
- The Indian tea industry is being developed and promoted by the Tea Board of India.
